How F1 engines work and their evolution from V10S to hybrid power units
The Formula One cars' Power Unit, the heart of the car, has six elements, including a 1.6-litre turbocharged combustion unit, which work together to produce about 1,000 horsepower. To power the race giants of the world, Formula One engines burn up to 100 kilograms of fuel. Get an inside look at the inner workings of the high-octane world of racing and discover how F1 engines work.

Source: Twitter
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Key takeaways
- Exploring how the F1 engines work
- What fuel does a Formula One car use?
- What are the specs of an F1 engine?
- How much cc does an F1 engine have?
- Why are F1 engines only 1.6 L?
- How much horsepower does an F1 engine produce?
- How many F1 engine manufacturers are there?
- What is the most powerful F1 engine ever?
Key takeaways
- The F1 car's Power Unit, which produces racing power, includes the internal combustion engine, turbocharger, electric motors, battery, and other components.
- Its other components include energy stores, control electronics, and exhaust systems.
- The sophisticated engine (I.C.E.) is a 1.6-litre V6 turbocharged internal combustion engine.
- The turbocharger generally compresses and drives air into the engine.
- There are two electric motors which harness and recover energy: the Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-H) and the Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-K).
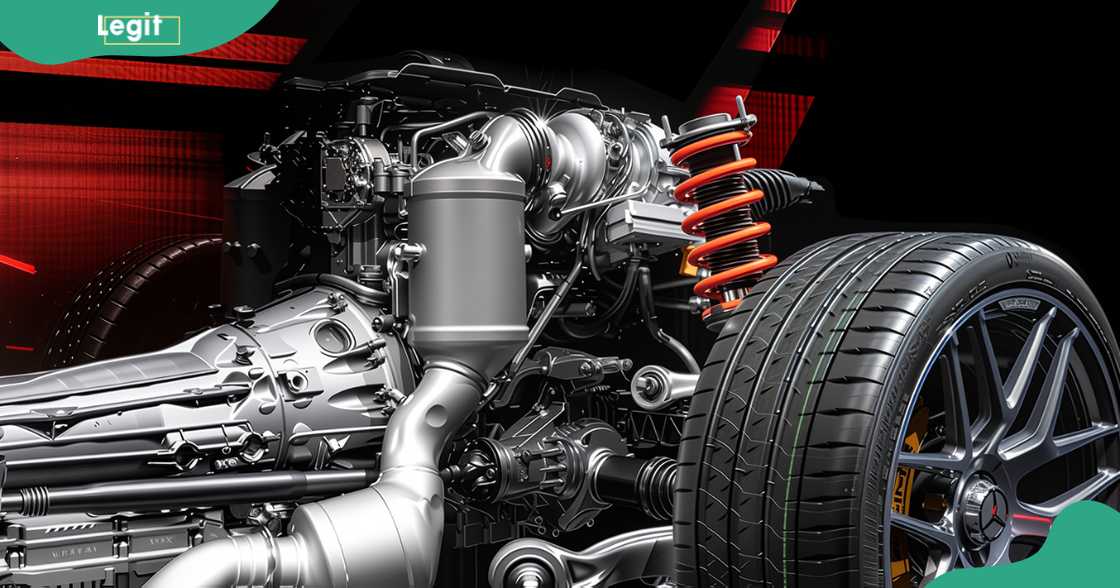
Exploring how the F1 engines work
The 2006 technical regulations introduced by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile introduced new engine specifications. After the 2006 season, Formula One transitioned from V10 engines to 8-cylinder engines arranged in a 90-degree V configuration, a move aimed at increasing engine efficiency, levelling the playing field, and promoting innovation.
In 2014, new changes to the F1 engine led to the adoption of the V6 configuration. The change introduced a new power unit consisting of a 1.6-litre V6 turbo engine that is still in use today. In 2026, new regulations on engine specifications, fuel, power and efficiency are expected.
The $10 million worth of F1 engine makes it one of the most valuable masterpieces in the engineering world. Explore the main components of the engine and learn how they work together to move the fastest cars in the world.
What type of engine is in an F1 car?

Source: Twitter
Formula One cars use a 1.6-litre V6 turbo hybrid engine. The engine generally produces over 1,000 brake horsepower. As a hybrid system, the engine also includes two electric motors, the MGU-K and MGU-H, that provide additional power and energy recovery.
The Internal Combustion Engine (I.C.E.) can generate around 850–900 horsepower with additional power output from the hybrid power unit. The I.C.E.'s rev limit is designed to reach up to 15,000 RPM.
How does the turbocharger in an F1 car work?

Source: Twitter
The turbocharger boosts the engine's power by compressing and forcing more air into the engine's combustion chamber. The compressed air increases the amount of oxygen for combustion, generating more power and torque.
To harness and drive air, the turbocharger uses the kinetic energy of exhaust gases to spin the turbine wheel. The turbine is mechanically connected to the compressor wheel that pulls and compresses air from the atmosphere.
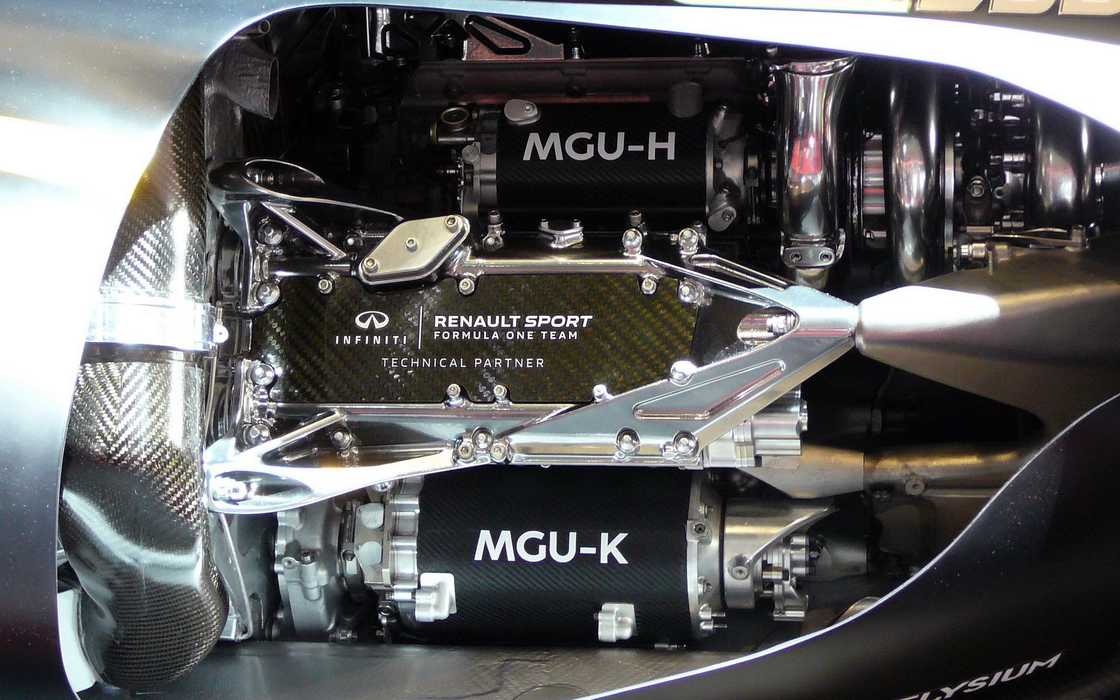
How do the motor generator units work in an F1 car?
Source: Twitter
Two crucial components of the power unit are electric motors that also function as generators. The Motor Generator Units (MGU-K and MGU-H) recover and deliver supplementary energy, boosting vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
The Motor Generator Unit-Kinetic (MGU-K) converts kinetic energy when the car slows down, converting it into electrical energy, which can either be stored or used to power the engine during acceleration.
The Motor Generator Unit-Heat (MGU-H) retrieves heat energy from the exhaust and uses it to generate electrical energy that can be stored in the battery or utilised directly. The MGU-H also acts as a motor, spinning the turbocharger.
How does the energy recovery system in an F1 car work?

Source: Facebook
Like its name suggests, the Energy Recovery Systems (ERS) recovers lost energy and reuses it to boost performance. The ERS recovers energy from two sources: braking through the MGU-K and the heat of the turbocharger through the MGU-H. This stored energy is then used by Formula One drivers to power the vehicle for acceleration and overtaking.
What are the control electronics in an F1 car?

Source: Twitter
The Control Electronics Module (CE) is widely regarded as the heart of the hybrid engine system. It links both motor generator units by managing the energy transfer between them and controls the Energy Recovery Systems (ERS).
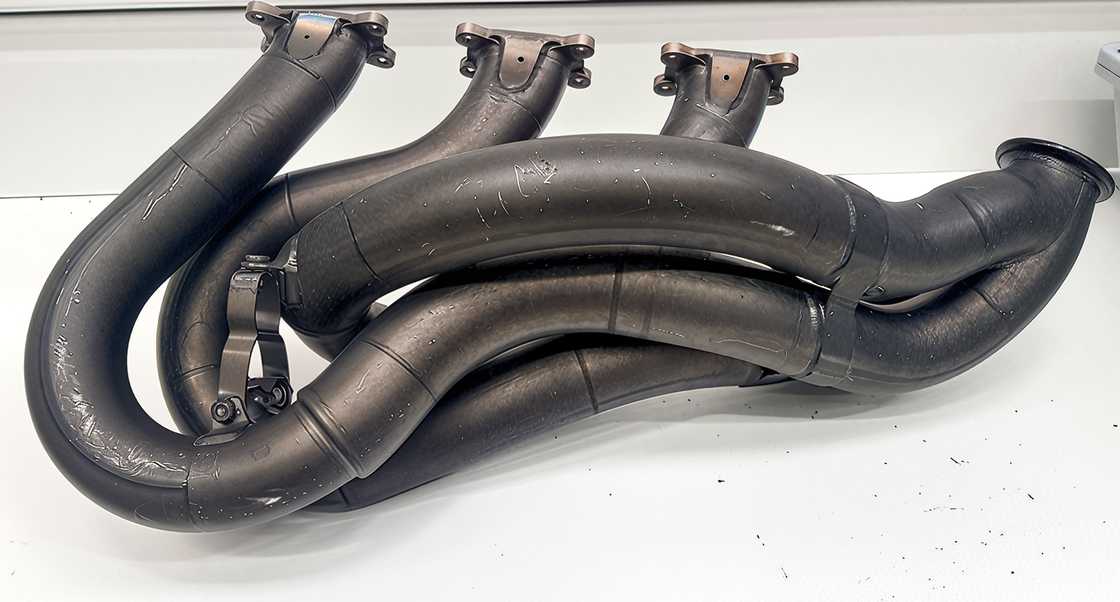
How do the Formula One exhaust systems work?

Source: Twitter
Formula One exhaust systems are highly engineered to remove exhaust gases. This role helps to optimise engine function and performance.
The exhaust system begins with the primary exhaust pipes from each cylinder in the engine. The pipes collect and carry the exhaust gases from the combustion chamber to secondary pipes that go into the turbocharger. The tailpipe comes from the turbocharger and carries the gases out of the car.
What fuel does a Formula One car use?
As of May 2025, Formula One cars use a renewable fuel, E10 petrol, that contains a blend of 90% petrol and 10% renewable ethanol. The blend is designed to reduce the use of fossil fuels in the field and promote the use of sustainable fuels.
What are the specs of an F1 engine?
F1 engines are 1.6-litre, 90-degree V6 turbocharged engines with a 80mm bore and 53mm stroke. Here are the specifications of the six-cylinder internal combustion engine as per the FIA:
- Engine capacity: 1,600 litres
- Number of cylinders: 6
- Bank angle: 90 degrees
- Number of valves: 24
- Maximum internal combustion engine RPM: 15,000 RPM
- Fuel injection mode: High pressure direct with a maximum 500 bar pressure and one injection per cylinder
- Fuel flow rate: 100 kg/hour above 10,500 RPM
- Turbocharger type: Single-stage compressor with exhaust turbine on a common shaft
- Maximum exhaust turbine RPM: 125,000 RPM
How much cc does an F1 engine have?
F1 engines have a displacement of 1.6 litres, which is equivalent to 1600 cubic centimetres (cc). In the upcoming 2026 updates, the FIA is expected to make significant changes that will introduce a smaller engine.
Why are F1 engines only 1.6 L?
This is believed to allow engineers to create smaller and more fuel-efficient engines. In addition to meeting strict FIA regulations, the move was reportedly put in place to manage development costs.
Read also
Fascinating details about Google Pixel 3 XL: Its features, specs, reviews, price, where to buy
How much horsepower does an F1 engine produce?
Typically, a Formula 1 engine produces approximately 1,000 horsepower. This output can vary slightly between teams. Additionally, during various portions of a race, F1 cars can operate with 850 horsepower to regenerate kinetic energy and achieve 1,000 horsepower when full power is deployed.
How many F1 engine manufacturers are there?
There are four engine manufacturers in Formula 1: Ferrari, Mercedes, Honda (Red Bull Powertrains), and Renault. These engines produce some of the highest horsepower in cars for private and competitive use.
What is the most powerful F1 engine ever?
The 1986 BMW M12/13 turbo engine is widely considered the most powerful F1 engine ever produced. The super engine capable of producing up to 1,400 horsepower generated 1,280 hp in 1983 and 1,350 hp in 1986 during qualifying tests at 11,000 RPM. While in use at Monza in the 1986 Italian Grand Prix, the car reached 352.22 kph (219 mph).
Understanding how the FI engine works inspires an unspoken appreciation for automotive engineering and innovation. The Formula One Power Unit's components all work together to help drivers achieve top speeds while making human achievement possible.
Legit.ng has recently published an article ranking and comparing the speeds of NASCAR and Formula One cars. For years, heavy debate has dominated the racing world, pitting NASCAR fans against those of Formula One.
While the fastest records for NASCAR stand at 212.809 miles, Formula One dominates its American counterparts with top speeds of 231.4 miles per hour. Explore the fast world of racing and compare past performances and official metrics.
Proofreading by Kola Muhammed, copy editor at Legit.ng.
Source: Legit.ng







