20 important historical events that changed the world
Numerous historical events affected the world and changed everything. While some happened a long time ago, others are recent, and they have all affected everyone in one way or the other. Discover some of the top and most talked about important historical events that changed the world.

Source: Getty Images
Various events have occurred throughout history that have eternally altered the direction of everyone's lives. Some have positive impacts, and others have had a drastic negative impact that is still remembered to date. Here are some of the most influential events in history you ought to know.
20 historical events that changed the world
Major historical moments that changed the world reshaped societies and economies. They led to profound societal transformations that influenced the modern world in various ways.
20. The Black Death (14th century)
The Black Death is one of the most important events in world history. It was a plague pandemic that struck Europe and Asia in the mid-1300s. The disease originated in central Asia and was taken to the Crimea by Mongol warriors and traders.
The Black Death led to a massive and rapid decline in the population of Europe. It is estimated that between 25 million to 50 million people, or roughly one-third of Europe's population, perished during the pandemic.
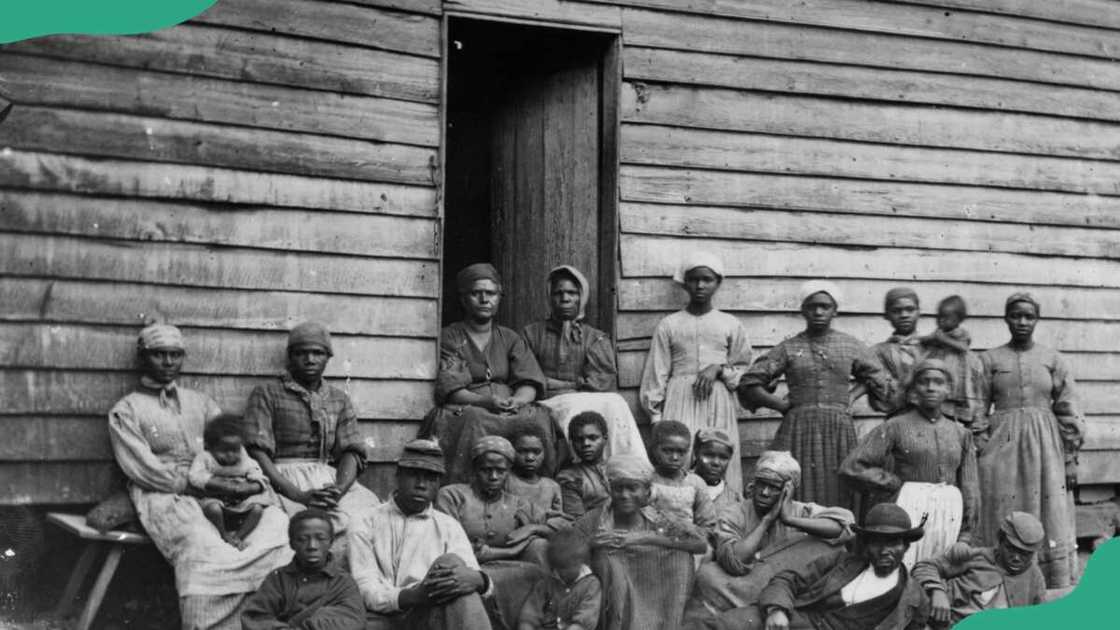
19. Transatlantic slave trade (16th and 19th centuries)
This was a global slave trade that led to the transportation and exploitation of over 10 million enslaved Africans. It was a brutal and inhumane system of forced labour that had a profound impact on Africa, the Americas, and Europe.
Enslaved Africans cultivated cash crops like sugar, tobacco, cotton, and rice, which were exported to Europe. This system of forced labour was characterised by extreme brutality and dehumanisation.
18. The invention of Electricity (19th century)
Electricity is arguably the greatest invention in human history. It revolutionized numerous aspects of society, industry, and daily life. Electricity has been known since antiquity, but only in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Scientists like Benjamin Franklin, Alessandro Volta, and André-Marie Ampère made crucial contributions to the understanding of electricity and magnetism during this time. This marked a transformative period in history, leading to the electrification of society, industry, and transportation.
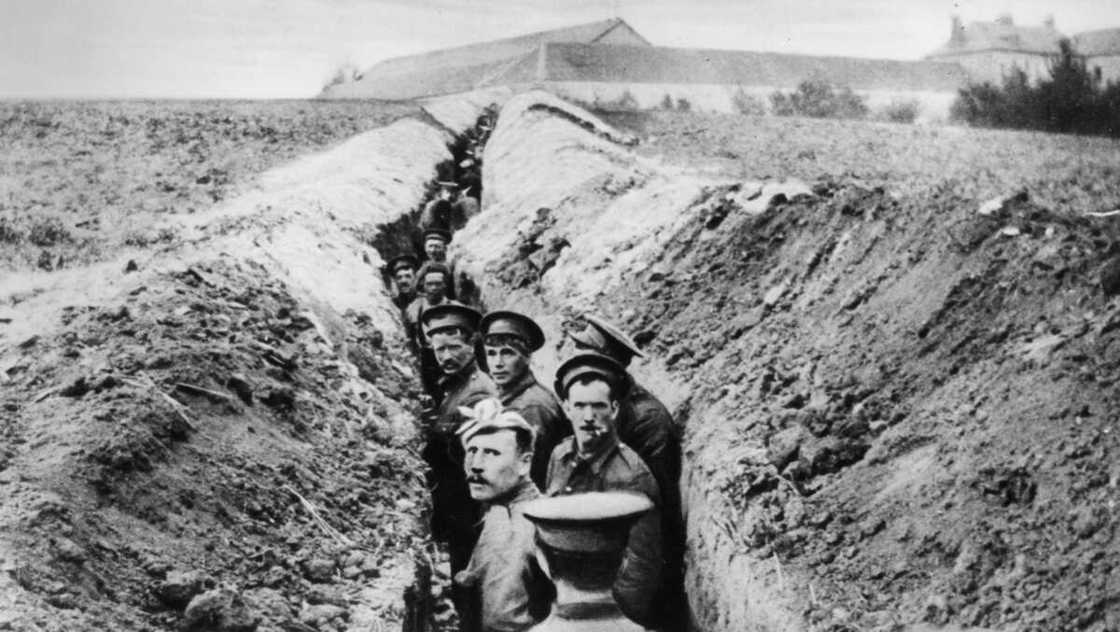
17. World War I (1914–1918)

Source: Getty Images
The First World War was a massive global war that lasted from 28 July 1914 until 11 November 1918. It is one of the major events that changed society. More than 100 countries from Europe, America, Asia, Australasia, and Africa were involved.
It is estimated that over 16 million people died as a direct result of the war, with millions more injured or left with long-lasting physical and psychological scars. It also led to the introduction of new modern military technologies such as guns, chemical weapons, and more.
16. Russian Revolution (October 1917)
The Russian Revolution was two separate incidents in 1917 but took root in 1905. At the time, the Russian Empire was experiencing deep social, economic, and political problems.
This revolution marked the beginning of a prolonged period of civil war in Russia. This led to the creation of the world's first communist state.
15. The reign of Adolf Hitler (1933–1945)
Adolf Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany in 1933. He quickly consolidated his authority and worked to eliminate political opposition.
His government initiated various public work projects and economic policies to reduce unemployment and stimulate the German economy. His ruling resulted in World War II, which was mass destruction.
14. The Great Depression (1929–1939)
The Great Depression was a huge economic crisis that hit many countries worldwide. It started when the stock prices in the United States dropped significantly. This event marked the longest, most severe, and most widespread economic downturn of the 20th century.
13. World War II (1939–1945)
World War II began when Germany, led by Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, prompting the UK and France to declare war on Germany. It had an estimated 70 million to 85 million casualties, making it one of the deadliest conflicts in history. It officially ended on 8 May 1945, when Germany surrendered unconditionally.
12. The Holocaust (1940–1945)
The Holocaust was the planned, systematic slaughter of millions of Jews and other minorities by Hitler's regime in Europe during World War II. Over six million Jews were shipped from all across Europe and subsequently killed in numerous concentration camps.
Jehovah's Witnesses, LGBTQs, Gypsies, and other minority groups were also victims of the Holocaust. Millions of people were displaced as a result of the catastrophe, including many Jews who had lost most or all of their family members and valuables.
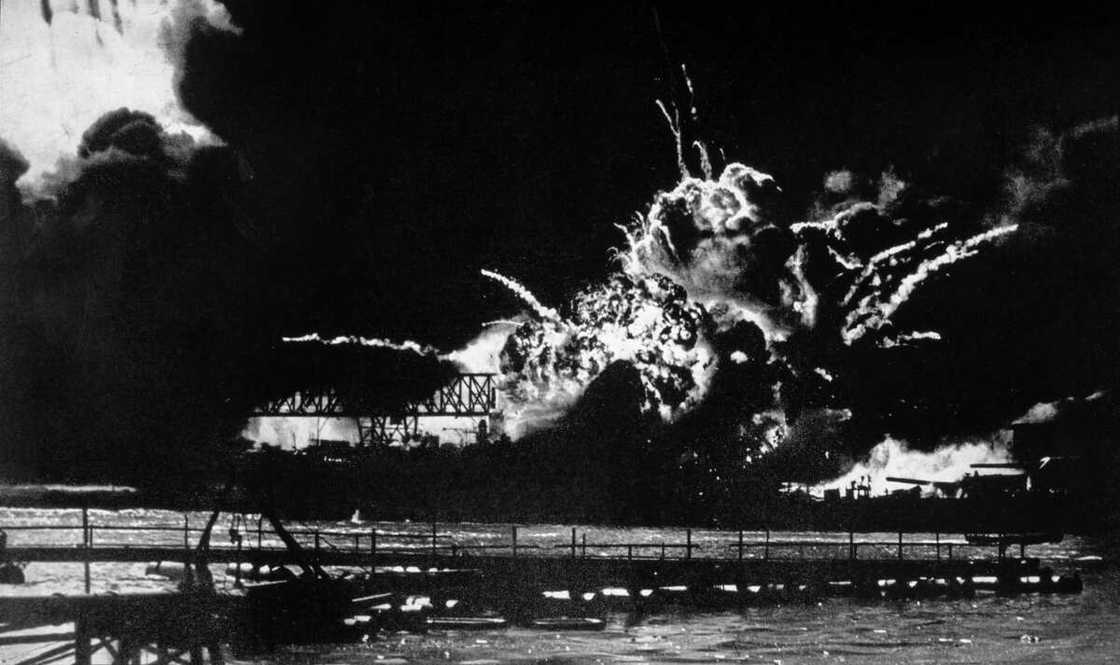
11. Attack on Pearl Harbor (1941)

Source: Getty Images
This was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States. It happened on 7 December 1941. A total of 19 USA military ships suffered damage and sunk, killing over 2400 people.
This occurred while the United States and Japan were officially engaged in diplomatic negotiations for possible Asian peace.
10. Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki (1945)
The uranium bombing occurred on 6 August 1945. It killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians. It also burnt around 70 per cent of all buildings, along with increased rates of cancer and chronic disease among the survivors.
9. Establishment of the United Nations (1945)
The United Nations was founded on 24 October 1945 after the World War II. It aimed to unite all the nations to promote peace and security.
The UN introduced the concept of collective security, where member states agreed to come to each other's aid in the event of aggression or armed conflict.
8. The Cold War (1946–1991)
The Cold War was a decades-long war for world power that pitted capitalist America against communist Russia. It was marked by intense political, economic, and military rivalry. Even though it did not last long, it left a legacy of tensions, alliances, and global security concerns that persist today.
7. People's Republic of China (1949–1976)
Maoist China and Red China refer to the period in China from the establishment of the People's Republic in 1949 to Mao's death in 1976. It is often divided into the Mao era and the post-Mao era.
It was during this era that the Great Chinese Famine, one of the worst famines in human history, occurred. The total number of deaths that occurred was over 50 million.
6. Discovery of HIV AIDS (1981)

Source: Getty Images
It is originally believed that HIV came from a virus on chimpanzees in West Africa in the 1930s. The virus later spread through Africa and other parts of the world.
But it wasn't until the early 1980s, when doctors started hearing about unusual cases of pneumonia, cancer, and other sicknesses, that people began to learn about HIV and AIDS.
In March 1982, Canada confirmed its first case of AIDS, and on 1 December 1988, the first World AIDS Day took place. By 1990, it was believed that around 8 million to 10 million people were living with HIV all over the world.
5. Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)
The fall of the Berlin Wall during the Peaceful Revolution on 9 November 1989 was an important turning point in world history. It was one of the events that precipitated the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe, preceded by the Polish Solidarity Movement.
Following the fall of the Berlin Wall, it became evident that the Soviet Union's rule over Eastern Europe could not be maintained, resulting in the dissolution of the Warsaw Pact and, finally, the reunification of Germany.
4. Invention of the Internet (1989)
The invention of the internet is among the historical events that made the world better. Tim Berners-Lee invented the internet in 1989. It has changed the way everyone communicates, stores information, and interacts with one another.
Today, the Internet is one of the most important modes of communication. It has become a necessity for survival. It has removed all social, economic, and physiological barriers and has had a significant impact on people's daily lives.
3. The dissolution of the Soviet Union (1991)
The breakdown of the Soviet Union (USSR) was a process of internal disintegration within the USSR. It resulted in the end of the country and its federal government as sovereign states. As a result, its component republics gained full autonomy on 26 December 1991.
Its collapse surprised many people, and the following economic breakdown resulted in a severe economic crisis. This led to a catastrophic decline in living standards in post-Soviet republics and the former Eastern Bloc, worse than the Great Depression.
2. 9/11 September attacks (2001)
The 9/11 September attacks are regarded as one of the moments that changed history. On 11 September 2001, there were four major attacks carried out by a group called al-Qaeda in the United States. Nineteen terrorists took control of four aeroplanes that were supposed to fly from the East Coast to California.
They crashed the first two planes into the Twin Towers in New York City and aimed the other two towards important places in or near Washington, D.C.
One of them hit the Pentagon, which is the main building for the U.S. Department of Defense, and the fourth plane crashed in a rural area in Pennsylvania.
The attacks killed 2,977 people from 93 nations: 2,753 people were killed in New York, 184 people were killed at the Pentagon, and 40 people were killed on Flight 93.
1. The Outbreak of Covid 19 (2019)
Source: Getty Images
In late December 2019, a new and unknown virus, the 2019 novel coronavirus, appeared in Wuhan, China. It caused a severe outbreak in many cities in China and quickly spread to other countries.
On 11 February 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) officially named the disease caused by this virus Coronavirus Disease-2019, or COVID-19. The effects of this outbreak have been unlike anything seen before, and it has had a profound impact worldwide.
People all over the world have been deeply affected. Many lost their lives, businesses suffered, and travel became very difficult. It's one of the events in history that changed the world. Many people are still feeling the effects of COVID-19 to this day.
Above are some of the historical events that changed the world. They left a long-lasting impression on everyone. Some of these events have affected how everyone lives today, both positively and negatively.
Legit.ng recently published an article about the history, population and language of the Republic of Cyprus. Cyprus stands out as a prominent tourist hotspot in the Mediterranean region. The official languages in the country are Greek and Turkish.
The island of Cyprus is located in the Mediterranean Sea. It is between 32° and 35° longitudes east and between 34° and 36° latitudes north. It is third by size in the Mediterranean region. Discover more fascinating facts about the nation.
Source: Legit.ng











