Nigerian Government structure
What are the three arms of government in Nigeria and their functions? Do you know this? Check out Nigerian government structure right here!

Nigeria is a federal state with 3 levels of state power. There are - federal, state and local levels of government in Nigeria. According to Nigerian constitution, Nigeria is a presidential republic.
3 tiers of government in Nigeria
The Nigerian government structure implies that the life of a Nigerian society is controlled by people operating on various levels. This means that some of them are responsible for power in the a whole state, others are authorized to oversee control and order only in some small areas, whereas some of them are to provide lawfulness, peace, and order on the territory of all the country.

Among the levels of government in Nigeria, the most powerful is definitely the federal level.
Federal level includes such bodies as:
1. Federal Executive Council;
2. National Defence Council;
3. National Security Council;
4. National Mass Media Commission;
5. National Economic Council.
Three arms of government in Nigeria and their functions
• The Federal Executive

• The Federal Legislature

• The Judiciary

Executive power
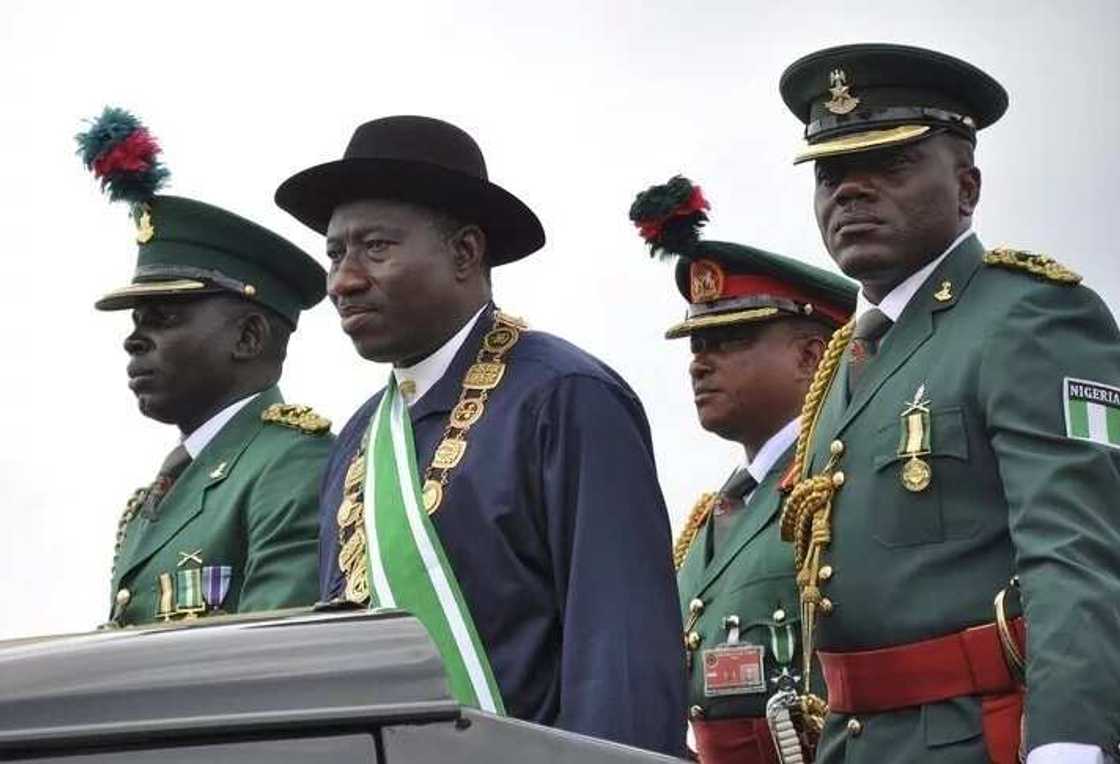
• President
The president of Nigeria is the head of state, at the same time he acts as the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. He takes this position after a nationwide election for a period of 4 years and can hold office no more than for two consecutive terms. In May 2006, the Senate refused to approve a constitutional amendment that would allow a president to be elected for a third term of power.

The president’s main function is to bear responsibility for the sound job of the Nigerian government system. He is also in charge of managing the training of the Army, equipment, and skillfulness.
He answers for the readiness of the country to withstand enemies and to provide security to every Nigerian resident.
The President doesn’t act as a member of the National Assembly, but he has the right to visit during its sessions and is required to approve laws in cooperation with this institution.
Nigeria current President position is held by Mohammadu Buhari.
• Vice-President

The Vice-President of Nigeria is the second most important official in the overall structure of the country's executive branch. The election of the vice president takes place at the presidential elections, as every candidate for the presidency goes to the elections along with a person who will hold the vice-presidential post. The vice-president is chosen from the same political party as the head of state himself.
READ ALSO: Solution to economic recession in Nigeria: 10 steps to be made
Under the constitution, his main function is to replace the president in case of his death, resignation or retirement.
Legislative power
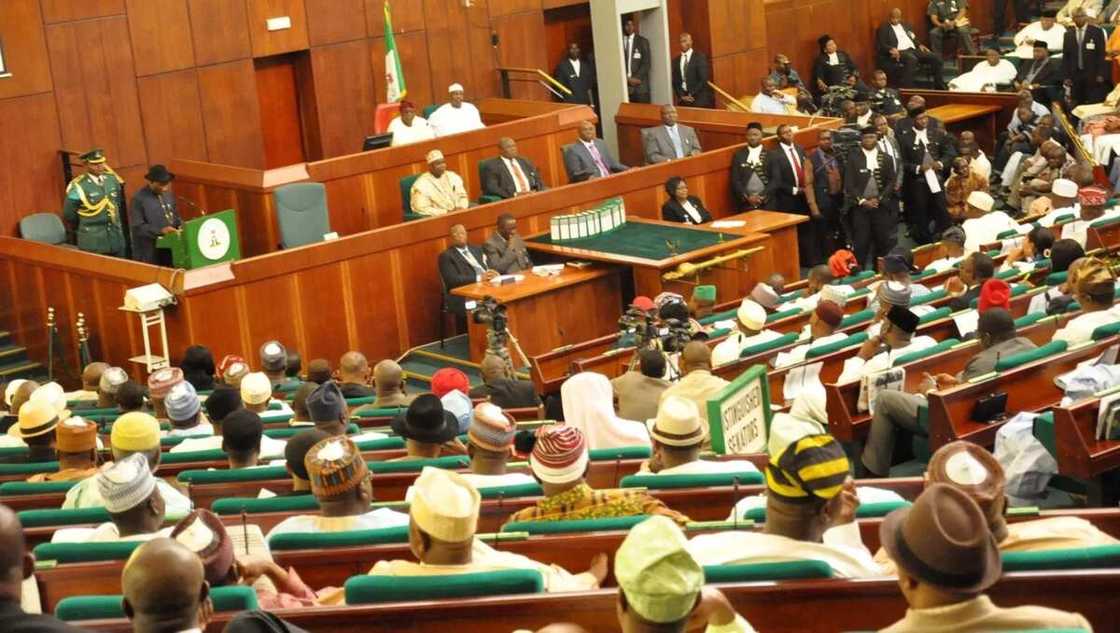

The Federal Legislature is represented by the bicameral National Assembly.
• Senate
The Upper chamber is the Senate (109 senators). Senators are elected by a majority system in 36 three-mandate and one single-mandate district. The Chairman of the Senate is elected by indirect voting by senators.

• The House of Representatives
The lower Chamber is The House of Representatives (360 seats). Deputies are elected by majority system. The term of office of all deputies is 4 years.
73 seats in the Senate and 213 in the House of Representatives are under the control of pro-presidential People's Democratic Party (NDP). The National Party (conservatives) – has 28 and 95 seats respectively.

Distribution of power between the Senate and the House of Representatives in Nigeria largely follows the USA pattern. The National Assembly adopts bills by a simple majority of votes in each of the two chambers for subsequent transfer to the President of Nigeria for signature, after which the bills come into force.
If the head of the state refuses to approve the bill, it returns to the Senate and House of Representatives for further confirmation. After the second voting, if 2/3 of each chamber supports the bill, it automatically becomes one of the acting federal laws.
Judicial branch
Nigerian Supreme Court is the most respectable judicial body which functions in the country. Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of Nigeria heads this body. In addition to this, there are also 13 associated judges appointed by the President of Nigeria according to the recommendation of the National Council of Judges. Sharia courts operate in a number of regions throughout the whole country.
The main task of the court is to ensure compliance with legislation, strengthening the rule of law and democracy. Its decisions are not subjected to further appeal and are considered as binding for the executive and legislative authorities.

The Supreme Court considers certain categories of cases as a court and also acts as the highest appellate court, reviewing judicial acts of both the Court of Appeal and other lower federal courts.
The Supreme Court consists of the Chief Judge of Nigeria and has 21 associated judges.
Now you are understand the Nigerian Government structure and know the three main arms of the Nigerian government which are The Federal Executive, The Federal Legislature, The Judiciary.
READ ALSO: What are main features of democracy?
Source: Legit.ng