7 classes of food with examples and functions - be in the know
We are what we eat, so eating healthy is important. The classes of food, with examples and functions, such as carbohydrates, are highlighted in this article, along with their sources and benefits to the body. Dr. Marion Nestle is a molecular biologist and nutritionist. She explains why classifying food is important for health and well-being.
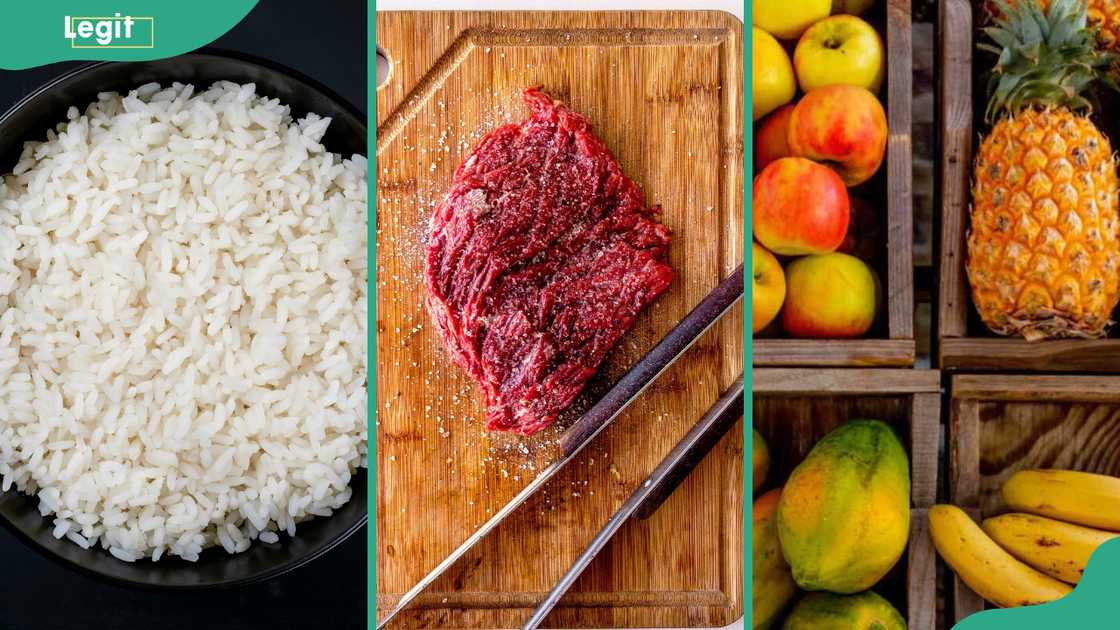

Source: UGC
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Key takeaways
- Classes of food with examples and functions
- Understanding food classification and nutrition, and their contribution to overall health
- What are the six classes of food with examples
- How many classes of food do we have?
- What are Michael Pollan's 7 rules for eating?
- What class of food is milk?
- What are examples of carbohydrates?
- Why is a balanced diet important for a child?
Key takeaways
- There are seven classes of food, each providing specific nutrients essential for the body.
- Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water all play unique roles in maintaining health.
- Understanding the classes of food with examples and functions helps in making balanced dietary choices.
- Eating a variety of foods from all seven classes supports growth, energy, and overall well-being.
Classes of food with examples and functions
There are seven major classes of food based on their nutrient properties:
- Carbohydrates are energy-providing nutrients present in potatoes, rice, wheat, maize, and various starches.
- Proteins, crucial for bodybuilding, can be sourced from meat, legumes, and dairy products.
- Fats are present in nuts and fruits such as avocados.
- Fiber, essential for digestion, is found in fruits and vegetables.
- Minerals, vital for improving bodily functions, are present in most foods, fruits, and vegetables.
- Vitamins, known for boosting immunity, can be found in fruits and vegetables.
- Water, necessary for creating bodily fluids, is present in fruits, juices, and other liquids.
What are the 7 classes of food and their functions?
The classification of food is based on macronutrients and micronutrients. Macronutrients usually include water, fiber, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. They are needed for our bodies in large quantities.
Micronutrients include vitamins and minerals. They are needed in our bodies in much smaller quantities. Macronutrients provide the body with the energy to live and prosper.
The body always needs some of these nutrients as they provide constant energy. People’s health deteriorates because of the imbalance of nutrients. There can also be a deficiency and an abundance of nutrients in our bodies. Here is a breakdown of the classes of food with pictures.
1. Carbohydrates
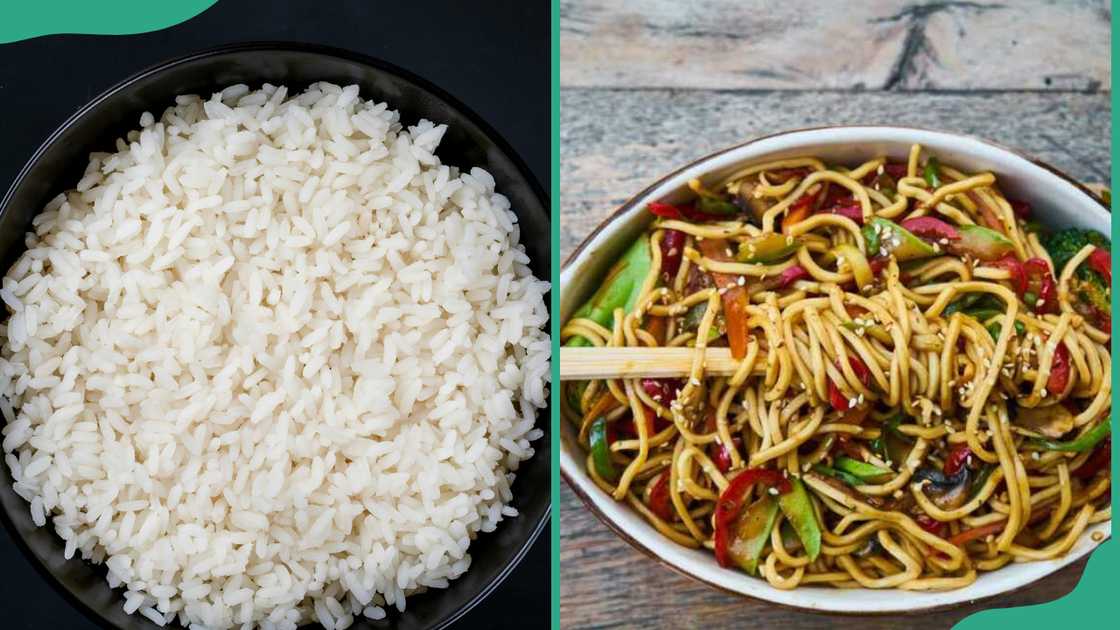

Source: UGC
Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are grouped by how many sugar units they have. These groups are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are found in rice, bread, pasta, noodles, and other grain products.
Polysaccharides are complex and take longer to digest. Simple sugars are absorbed quickly into the blood. Eating too many simple carbs can raise blood sugar and increase the risk of heart and blood vessel problems.
Carbs are always mentioned when discussing the four classes of food, along with proteins, fats, and vitamins.
2. Protein
Source: UGC
Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Nitrogen is vital for the amino acids our body needs. Proteins help build cells, keep muscles strong, and support metabolism. Most of our body structure is made of protein.
Each protein molecule contains thousands of amino acids. The body uses them to make new proteins and maintain existing ones. Proteins made by the body are called non-essential, while those we cannot make are essential.
All animals need essential proteins to survive. This nutrient is found in foods like beans, dairy products, fish, meat, and eggs.
3. Fats

Source: UGC
A fat molecule is made up of several fatty acids. These acids contain long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Fats are classified into saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats have all carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen.
Unsaturated fats have some double bonds between carbon atoms. Fats provide energy, help maintain body temperature, and assist in absorbing vitamins. They are found in various foods, like meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables, and nuts.
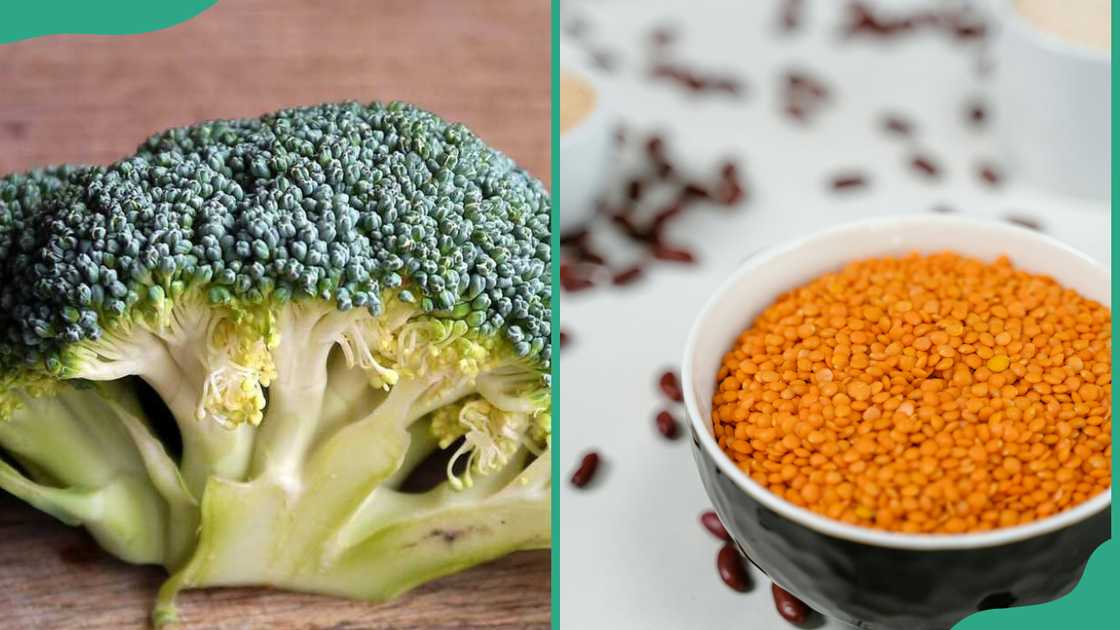
4. Fiber

Source: UGC
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot absorb. It is mostly made of cellulose, a large carbohydrate that cannot be digested because the body lacks the right enzymes.
Fiber is found in fruits like oranges and pears and in vegetables like broccoli and corn. It is also present in pulses such as beans and lentils, and in whole grains like cereals.
It helps keep the digestive system healthy and working properly. Fiber also helps control cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Eating enough fiber can reduce the risk of heart disease, bowel cancer, and diabetes.
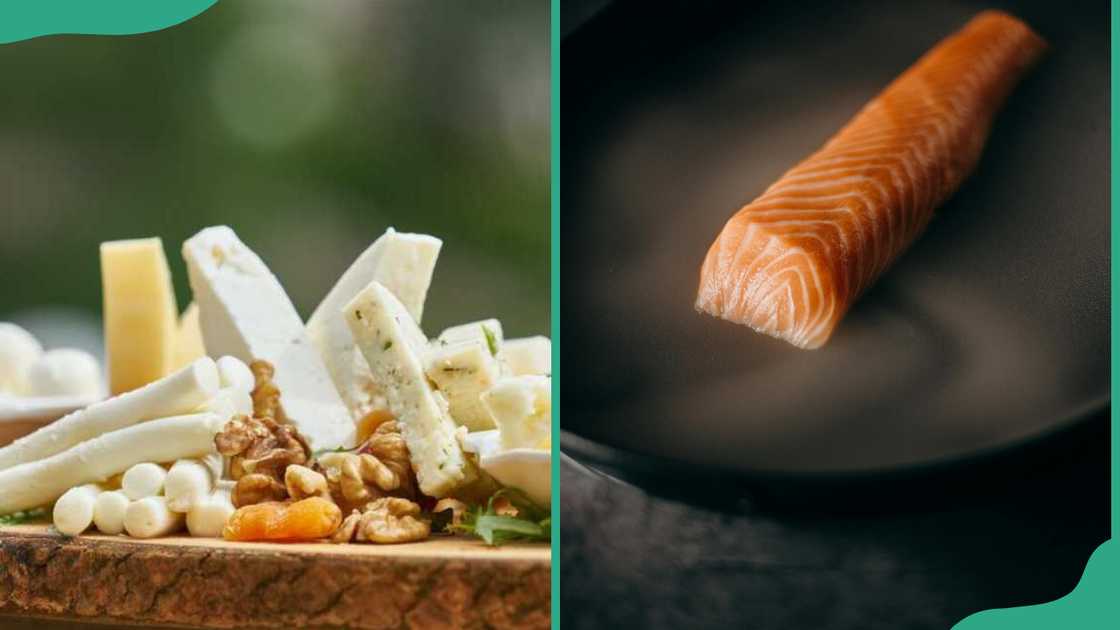
5. Minerals

Source: UGC
Minerals are chemical elements essential for the health of living things. Even in small amounts, the body needs them to stay healthy. Common minerals include calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc.
They are found in foods like cheese, as well as in meat, fish, poultry, and grains. Minerals have many roles, such as building strong bones, muscles, and teeth, carrying oxygen in the blood, and keeping body fluids balanced.
6. Vitamins

Source: UGC
Vitamins are nutrients needed in small amounts but are very important for the body. Examples include thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, pyridoxine, folic acid, cobalamin, and ascorbic acid.
Vitamins support the immune system and help the body stay healthy. They are found in many different foods all over the world.
7. Water

Source: UGC
Water is a vital part of our diet. The human body is made up of about 80% water. That is why we need water to stay alive and healthy. Water is made of hydrogen and oxygen, yet we cannot survive without it.
Its main roles include hydration, helping the body absorb nutrients, aiding digestion and metabolism, and regulating body temperature.
Understanding food classification and nutrition, and their contribution to overall health
During an interview with Dr. Marion Nestle, a molecular biologist, nutritionist, and public health advocate, Legit.ng got valuable insights on the significance of food classification and its impact on health.
Dr. Marion said the standard groups of various food types include fruits and vegetables, grains, meat and poultry, fish, dairy, and eggs, which are based on animal and plant differences and also nutritional contributions. She said:
A key tenet of nutrition is variety in food intake, both between and within groups. Different foods have different nutrients in different proportions. Eating a variety of whole, relatively unprocessed foods enables consumption of those with complementary nutrient compositions.
Importance of lesser-known classes of food
Dr. Marion said fungi and algae can be categorised under 'lesser-known' classes of food; however, they can also be classified under plants. She also highlights the category for ultra-processed foods—the ones best to avoid or consume in small amounts.
To maintain a balanced diet, Dr. Nestle advises eating a wide variety of foods from all food groups.
What are the six classes of food with examples
Below is a summary table of the 6 classes of food and their functions.
No | Classes of food | Sources | Functions |
1 | Carbohydrates | Grains, legumes, wheat, potatoes, cassava, maize, wheat, flour yams | Energy-giving nutrients |
2 | Protein | Egg, fish, beans, lentils, beef, yoghurt, cheese, nuts | Bodybuilding nutrients |
3 | Fats | Vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, fish | Helps your body absorb vital nutrients |
4 | Fiber | Broccoli, berries, dried fruits, chia seeds, raspberries | Necessary for digestion |
5 | Minerals | Cereals, bread, meat, fish, milk, dairy | Improving bodily functions |
6 | Vitamins | Nuts, fruit and vegetables, milk and dairy foods | Boost immunity |
Deficiencies of the 6 classes of food
The six classes of food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. If the body does not get enough of each:
- Carbohydrates - you may feel tired and have low energy.
- Proteins - your muscles may become weak and growth may slow.
- Fats - skin may become dry and the body may feel cold.
- Vitamins - you could get diseases like scurvy or rickets.
- Minerals - problems like anemia or weak bones can happen.
- Fiber - you may have constipation and digestive problems.
How many classes of food do we have?
There are seven main classes of nutrients that the body needs. Here are the classes of food with examples for primary school: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fibre, and water.
Below is an illustration of food nutrients and their sources and functions.

Source: Original
What are Michael Pollan's 7 rules for eating?
Michael Pollan, the author and food advocate, summarized his approach to healthy eating in seven simple rules. They are designed to guide people toward more natural, mindful, and balanced eating habits:
- Eat food. – Focus on real, whole foods, not processed products.
- Not too much. – Pay attention to portion sizes and avoid overeating.
- Mostly plants. – Emphasize vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
- Avoid food products containing ingredients unfamiliar or unpronounceable. – If you do not recognize it as real food, avoid it.
- Do not eat anything your great-grandmother would not recognize as food. – Choose traditional, minimally processed foods.
- Avoid foods that make health claims. – Foods marketed as “low-fat” or “diet” are often highly processed.
- Shop the peripheries of the supermarket. – The outer edges usually have fresh produce, dairy, meats, and whole foods; the center aisles contain more processed foods.
Pollan’s rules are simple but emphasize whole, minimally processed foods, portion control, and plant-based eating.
What class of food is milk?
Milk belongs to more than one class of food. It contains many nutrients. It is mainly a protein-rich food. It also provides fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
What are examples of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates provide energy for the body, but the type and quality of carbohydrates can vary. We have simple carbohydrates such as Honey, maple syrup and molasses. We also have Complex Carbohydrates, divided into grains, bread, starchy vegetables, and whole fruits.
Why is a balanced diet important for a child?
A balanced diet is crucial for children as it is fundamental to their overall growth, development, and well-being. It ensures that children receive a wide range of essential nutrients for their growth and development.
All seven classes of food provide nutrients needed for the body to function well. You must eat all the necessary elements to stay healthy. Learning the classes of food with examples and functions helps you understand how to balance fats, carbohydrates, water, and other nutrients.
Legit.ng recently published an article on how to prepare chicken curry sauce in Nigeria. Chicken curry sauce is a delicacy, and there are numerous ways to prepare it.
Nigerians utilize several chicken curry sauce recipes because they enjoy experimenting with diverse flavours. After learning how to prepare curry sauce, you can design a customized dish for your family.
Source: Legit.ng

Jackline Wangare (Lifestyle writer) Jackline Simwa is a content writer at Legit.ng, where she has worked since mid-2021. She tackles diverse topics, including finance, entertainment, sports, and lifestyle. Previously, she worked at The Campanile by Kenyatta University. She has more than five years in writing. Jackline graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in Economics (2019) and a Diploma in Marketing (2015) from Kenyatta University. In 2023, Jackline finished the AFP course on Digital Investigation Techniques and Google News Initiative course in 2024. Email: simwajackie2022@gmail.com.

Adrianna Simwa (Lifestyle writer) Adrianna Simwa is a content writer at Legit.ng where she has worked since mid-2022. She has written for many periodicals on a variety of subjects, including news, celebrities, and lifestyle, for more than three years. She has worked for The Hoth, The Standard Group and Triple P Media. Adrianna graduated from Nairobi University with a Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) in 2020. In 2023, Simwa finished the AFP course on Digital Investigation Techniques. You can reach her through her email: adriannasimwa@gmail.com









